Contents
Introduction
In the digital age, the Internet of Things has emerged as a groundbreaking concept, revolutionizing the way we interact with our surroundings. In this comprehensive review, we will look at its essence, intricacies, applications, benefits and potential problems.
Understanding the Basics: What is IoT?
At its core, the Internet of Things encompasses the seamless interconnection of physical devices through the internet, enabling them to gather, share, and leverage data. This network of devices, equipped with sensors and software, transcends traditional communication methods, ushering in a new era of interaction and control.
Software for IoT
The functionality hinges on software that facilitates communication, data processing, and decision-making. These software platforms enable devices to interact, transmit data, and execute actions in response to user commands or environmental triggers.
IoT software can be classified into four main categories:
- Connectivity platforms: These platforms provide the infrastructure for connecting IoT devices to the internet and to each other. They typically support a variety of communication protocols, such as WiFi, Bluetooth, and cellular.
- Device management platforms: These platforms help organizations to manage their IoT devices, including provisioning, monitoring, and updating them. They also provide features for security and compliance.
- Application enablement platforms: These platforms provide the tools and frameworks for developers to create IoT applications. They typically include features for data collection, visualization, and analytics.
- Analytics platforms: These platforms help organizations to make sense of the data generated by their IoT devices. They provide features for data warehousing, analysis, and reporting.
Hardware for IoT
The hardware aspect includes the tangible components that constitute connected devices. These components range from sensors that capture data to processors that perform computations and actuators that trigger specific responses.
Here are some of the common types of IoT hardware:
- Sensors collect data from the physical world. They can measure a variety of things, such as temperature, humidity, light, motion, and sound.
- Actuators take action based on data from sensors. They can control things like lights, doors, valves, and motors.
- Gateways connect IoT devices to the internet. They translate the data from IoT devices into a format that can be understood by the internet.
- Routers route data between different networks. They are essential for connecting IoT devices to each other and to the internet.
- Other devices: There are many other types of devices that can be used in IoT systems. Some common examples include:
- Microcontrollers are responsible for collecting data from sensors, processing data, and controlling actuators.
- Radio modules are used to transmit data between IoT devices. They can use a variety of radio protocols, such as WiFi, Bluetooth, and Zigbee.
- Power supplies provide power to IoT devices. They can be battery-powered, AC-powered, or solar-powered.
How Does The Internet Of Things Work?
IoT operates through a network of devices that communicate and collaborate in real-time. Data collected by sensors is transmitted to centralized systems or cloud platforms for processing and analysis. Insights drawn from this data facilitate informed decision-making and automation of tasks.
Types of IoT
IoT technology continues to develop, and we can expect numerous types of IoT in the future. Let’s consider the most common types:
Consumer IoT (CIoT):
CIoT is used for everyday consumer products, such as smart home devices, wearables, and fitness trackers. CIoT devices are typically low-cost and easy to use, and they are designed to connect to the internet and collect data about the user’s environment or activities.
Industrial IoT(IIoT):
Industries are using it to optimize operations and increase productivity. Manufacturing processes, supply chains, and equipment monitoring benefit from real-time data analysis. IIoT devices are typically more expensive and complex than consumer electronics devices, but they are able to collect and process more data. IIoT devices are used to improve efficiency, safety, and productivity in industrial settings.
Enterprise IoT:
Enterprise IoT is used in businesses and organizations. Enterprise IoT devices are used to collect data about operations, assets, and customers. This data can be used to improve decision-making, optimize processes, and provide better customer service.
Critical IoT:
Critical IoT is used in applications where reliability and security are critical, such as healthcare, transportation, and defense. Critical IoT devices are typically designed to be highly reliable and secure. They are also typically connected to a private network to protect their data from unauthorized access.
Agricultural IoT:
Agricultural IoT is used to monitor crops, livestock, and other agricultural assets. This data can be used to improve crop yields, optimize livestock production, and reduce food waste.
Smart city IoT:
Smart city IoT is the use of IoT technology to improve the efficiency and sustainability of cities. It is used to monitor traffic, energy consumption, and other urban infrastructure. This data can be used to improve traffic flow, reduce energy consumption, and create a more livable city.
Let’s consider the most trendy industries that currently adopt IoT technology:
IoT in Healthcare
In healthcare, IoT devices monitor patients’ vital signs, enabling remote monitoring, timely interventions, and improved patient outcomes.
See how AJProTech is revolutionizing lung health analysis with its latest innovation, the Lungs Health Analyzer.
IoT in Sports
In Sports, IoT is already being used to improve the performance of athletes, enhance the fan experience, and make sports more sustainable. As IoT continues to develop, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of this technology in the sports world.
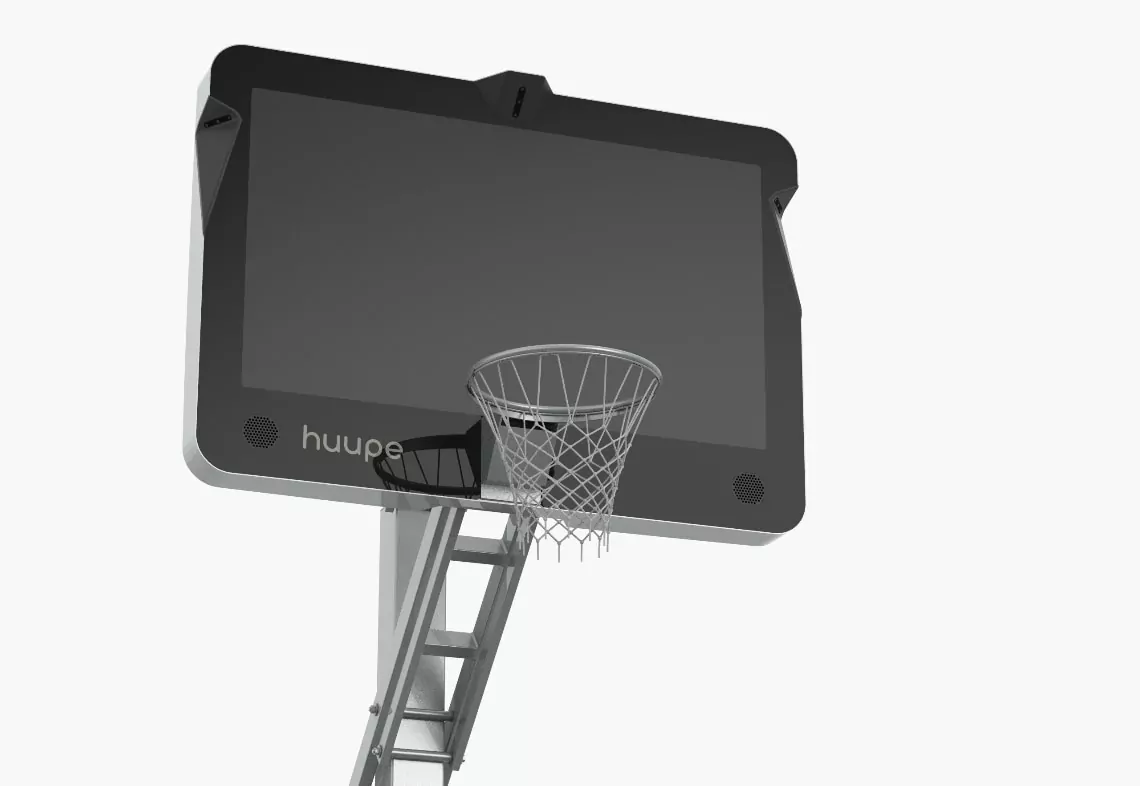
See how AJProTech’s innovative technologies are transforming traditional basketball sports on Huupe. Huupe is a revolutionary cutting-edge product for sports enthusiasts and athletes.
IoT in EEG and Neuroscience
The combination of IoT and EEG technology has the potential to revolutionize the field of neuroscience. It will allow researchers to study brain function in a more detailed and comprehensive way. It will also allow BCIs to be used in a wider range of applications, such as rehabilitation, gaming, and entertainment.
Here are some specific examples of how IoT is being used in neuroscience and EEG:
EEG headsets: IoT-enabled EEG headsets are being used to collect EEG data from users in real-time. This data can be used to study brain function in a variety of contexts, such as sleep, learning, and mental illness.
BCIs: IoT-enabled BCIs are being used to control computers and other devices with brain signals. This technology has the potential to revolutionize the way that people with disabilities interact with the world around them.
EEG sensors in wearables: IoT-enabled wearables, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, are being used to collect EEG data from users. This data can be used to track sleep quality, stress levels, and other aspects of mental health.
IoT is a rapidly evolving field with the potential to revolutionize the way that we study and interact with the brain. As IoT technology continues to develop, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of this technology in neuroscience and EEG.
IoT in VR/AR
When IoT and VR are combined, they can create new and immersive experiences that were not possible before. For example, IoT sensors can be used to track the user’s movements and environment in VR, and this data can be used to create a more realistic and interactive experience.
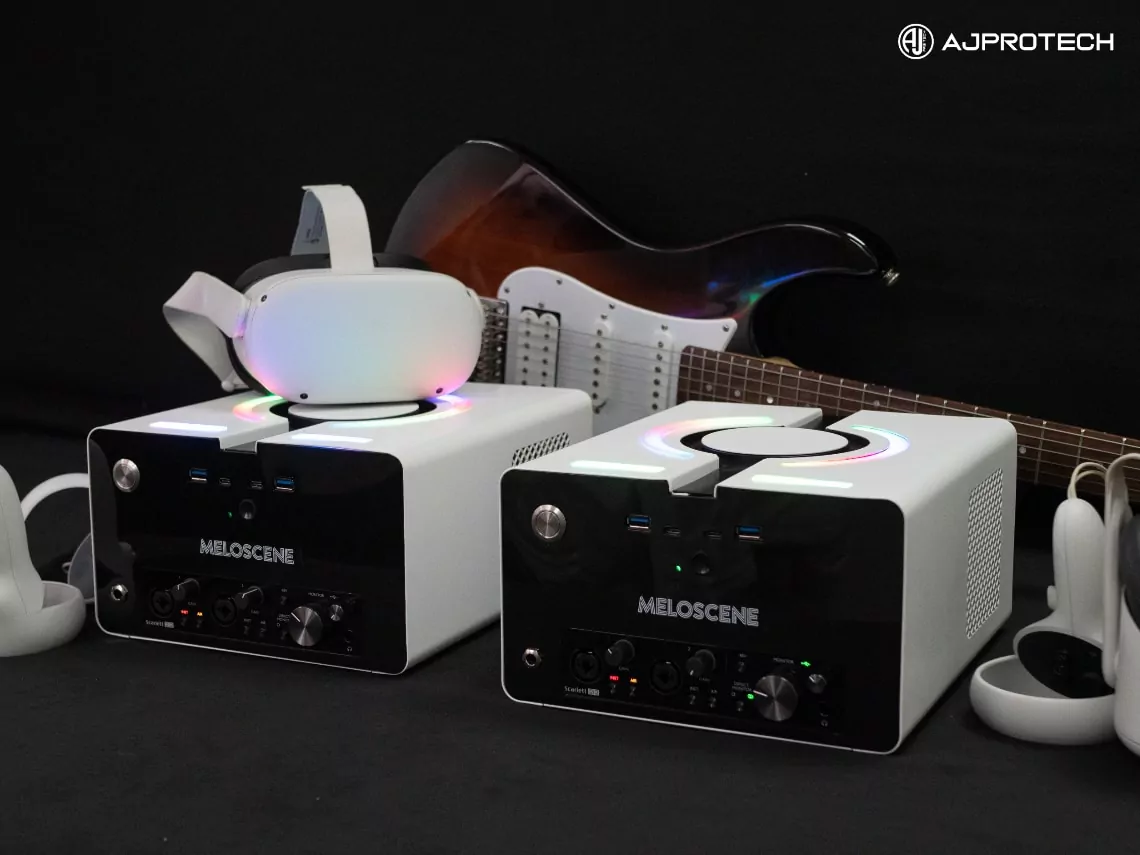
Check out our unique case where VR is embodied in the IoT device Meloscene Scenekey. This IoT solution offers a VR room for performing and recording music in extended reality. But that’s not all – you can also play in a band in extended reality, even if your team is located in different parts of the world.
Benefits of the internet of things
The benefits of IoT are far-reaching. It offers streamlined processes, data-driven decision-making, improved resource utilization, and enhanced user experiences. Smart homes provide comfort and energy efficiency, while industries achieve greater operational efficiency.
Internet of Things Development
Development involves creating connected devices, software platforms, and applications. It encompasses hardware design, software coding, iot network configuration, and data management to bring concepts to life.
IoT Security: Challenges and Measures
While it brings numerous advantages, security concerns are paramount. The proliferation of interconnected devices opens avenues for cyber threats. Ensuring robust encryption, regular updates, and user awareness are crucial to mitigating risks.
The Future of IoT: What’s Next?
The trajectory points toward continued growth and innovation. As technology advances, internet of things applications will expand to diverse sectors, driving efficiency, sustainability, and connectivity across industries.
FAQ:
What exactly is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the interconnected network of physical objects, devices, vehicles, buildings, and more, embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity capabilities. This enables them to collect and exchange data over the internet, fostering communication and interaction between these objects and their users.
How does IoT work?
IoT devices, equipped with sensors, gather data from their surroundings. This data is then transmitted through networks to cloud platforms or centralized systems. Here, the data is processed, analyzed, and often used to trigger specific actions or provide insights to users through various interfaces.
What are some examples of IoT devices?
IoT devices span a wide spectrum, from the everyday to the extraordinary. Smart thermostats, wearable fitness trackers, connected refrigerators, industrial sensors, self-driving cars, and even smart city infrastructure like traffic lights and waste management systems are all IoT examples of devices.
What are the security risks of IoT?
IoT devices introduce security challenges due to their interconnected nature. Vulnerabilities can arise from weakness.
How can IoT security risks be mitigated?
IoT security risks can be mitigated through the following strategies:
Secure Device Management:
- Implement strong authentication and individual credentials for devices.
- Regularly update and patch device firmware and software.
Data Protection:
- Encrypt data in transit and at rest.
- Use secure communication protocols.
Network Segmentation:
- Isolate devices in separate networks.
- Employ firewalls and access controls to restrict communication.
Regular Assessments:
- Conduct vulnerability assessments and penetration testing.
User Education:
- Train users about security best practices.
- Raise awareness about social engineering threats.
Vendor Scrutiny:
- Choose reputable IoT device manufacturers.
- Assess third-party components for vulnerabilities.
Incident Response Plan:
- Develop a plan to respond to security breaches.
- Test and update the plan regularly.
Regulatory Compliance:
- Adhere to data protection regulations and industry standards.
Physical Security:
- Secure physical access to devices to prevent tampering.
- Cloud Security.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Internet of Things represents a paradigm shift in how devices communicate and collaborate. From smart homes to industrial sectors and healthcare, impact is pervasive. As we navigate the challenges and harness the benefits, transformative potential continues to unfold. Embrace the future of interconnected technology and explore the endless possibilities that IoT offers.